
The Dynamic Crypto Industry Building A Bitcoin-Backed Monetary System. Consider Banks Without Bankers

One of the main advantages of cryptocurrency is the independence it offers by enabling individuals to become their own bank. With cryptocurrency, you have complete control and ownership of your assets, whereas traditional banks have technical ownership over the assets you store with them. While the concept of being your own bank is impressive, critics argue that specialized crypto banks may be necessary for crypto to compete effectively with the established financial system.
This article summarizes a report outlining a method for establishing financial institutions without the need for traditional bankers. This method utilizes Bitcoin to achieve this goal, and the approach aligns with the broader aim of revolutionizing the financial sector by harnessing the power of cryptocurrency to replace the existing flawed monetary system.
Banks Without Bankers Prioritizing User Agency
Today's summary is of a report called "Banks without Bankers," released by AxiomBTC, a venture capital firm focused on Bitcoin. The report starts with a powerful quote from Hal Finney, a pioneering Bitcoin developer who received the first Bitcoin transaction. In the quote, Hal Finney envisions a future where BTC is crucial in reshaping the banking system.

Source: Axiom.BTC
In the report authored by Eric Yakes, he explores two potential outcomes for the future of Bitcoin. On one end of the spectrum, all BTC could be held in custody by third parties like banks, with individuals trading receipts instead. This is similar to the historical concept of fiat money, representing a gold claim held by a bank. On the other end of the spectrum, Bitcoin could become a widely-used medium of exchange, with individuals directly transacting with each other and BTC effectively replacing money and its associated functions.
The idea presented is impractical due to several factors. Bitcoin faces limitations in scaling at its core level and is missing the necessary smart contract capabilities for sophisticated financial operations. Similarly, the scenario where all BTC is held in custody is not feasible because some BTC holders prefer to maintain control over their cryptocurrency assets through self-custody and peer-to-peer transactions. Therefore, it can be reasoned that the future of Bitcoin lies in a balance between custody services and individual self-custody practices.
Eric points out in the report that advancing technologies in the Bitcoin sector will allow for striking this balance carefully, emphasizing prioritizing greater peer-to-peer interactions. This approach is logical, as Bitcoin was initially designed to distance itself from traditional financial institutions like banks. In other words, the primary goal of Bitcoin was to remove the reliance on third parties to safeguard assets, hence the inherent trustless quality of cryptocurrency.
Eric contends that not all trust is misplaced, as it's crucial to place confidence in the right individuals and ensure their motivations align. He reinforces this notion by highlighting evolutionary biology findings emphasizing communities' importance in survival and reproduction. He then draws parallels between these findings and the contemporary financial system, where community-oriented banks are less likely to fail.
Eric believes that community banks are restricted by their geographical reach, meaning those nearby can only access their benefits. This limitation stems from the physical constraints of the world. In contrast, the digital realm knows no boundaries or distances. Eric suggests that with the appropriate technology, Bitcoin could enable the establishment of a digital community bank that transcends geographical limitations.
A critical technological component is multi-signature (mult-sig) wallets, which enable multiple individuals to manage a single Bitcoin wallet. In essence, multi-sig wallets enable the creation of conditions that allow this shared wallet to spend BTC. This technology allows the establishment of a ‘federation,’ which Eric defines as a system where “multiple participants hold keys that are useless in isolation, but can be combined to produce a signature that is required to make a transaction.”
Source: https://fedimint.org/
Fedimint: A Decentralized Solution
The first part of the report introduces a federated network called Fedimint. It’s designed to address issues related to trust in third parties and the complexities of self-custody. The concept is to rely on your community for trust rather than depending on external entities or solely yourself for technical matters of self-custody. A combination of four underlying technologies powers Fedimint;
- Federations can be considered a collection of reliable, trusted nodes that work together to operate a network. These nodes are responsible for maintaining the integrity of the system.
- Multi-sig wallets, as previously mentioned above.
- A privacy-preserving digital currency called eCash which is backed by BTC.
- The Lightning Network: (LN) A layer two protocol on the Bitcoin Network.
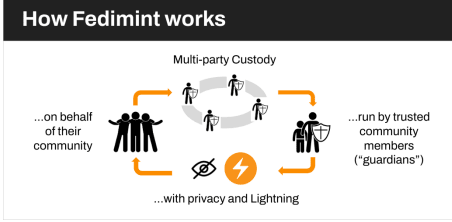
At the protocol level, Fedimint consists of four participants;
- Users who can mint, redeem, and transfer eCash.
- Guardians that function as nodes on the network and facilitate the minting, redemption, and transfer of eCash.
- Gateways that can be simply understood as nodes that make eCash transferable on the Lightning Network.
- Modules, which are the applications on Fedimint.
Each Fedimint system has three built-in modules: BTC, eCash, and a connector for integrating with the Lightning Network. Users can expand the functionality of their Fediment system by adding extra modules like eCash payments and advanced eCash exchanges. Fedimint networks have the potential to function as virtual community banks, operate independently, and manage financial transactions without traditional bankers. The community-driven infrastructure allows seamless interaction with other Bitcoin-based Fedimint networks.
Source: Bitcoin magazine
Eric explores an alternative method in which Bitcoin could replace traditional banks, this time through utilizing a different protocol known as Cashu. Like Fedimint, Cashu utilizes a privacy-preserving eCash supported by Bitcoin, crypto’s store of value. However, Cashu is notably more centralized, operating on a single server. The trade-off is that the centralized aspect allows for efficient monitoring of the eCash circulation without jeopardizing user privacy, which contrasts with the challenge faced by Fedimints, where tracking the supply of eCash is hindered by its inherent privacy features.
Money and e-Cash
In the second part of the report, Eric asserts that a single form of money will eventually become the universal standard for transactions. He argues, “In theory, market participants converge upon a monetary standard. In a perfect world, there would only be one form of money. Yet, throughout history, this has never been the case.” Eric provides three explanations for the historical absence of a singular form of money.
The first is opacity or the general lack of information about other currencies available to the average person. Another reason is governments' desire to control their own currencies, a concept called sovereign coercion. The third factor to consider is the trade-offs associated with money. For instance, in today's world, real estate is often viewed as a more reliable store of value compared to the US dollar, as explained by Eric.
For reference, the concept of money refers to a medium that holds value, while currency is a means of exchange used to purchase goods and services. This video clarifies the distinction between the two, highlighting how they were once equivalent when backed by gold. However, once currency was no longer tied to gold, it lost its value as a form of money. Despite this shift, we continue to operate under the belief that we are working for money through indoctrination, both explicitly and implicitly.
Eric explains we are not out of the woods regarding BTC being the complete solution to this problem. He notes that although BTC addresses numerous obstacles that have previously hindered the widespread adoption of a single currency, it faces its own obstacles regarding scalability (speed) and privacy. The Lightning Network is a potential remedy for Bitcoin's scalability issue, while eCash is a solution for enhancing Bitcoin's privacy.
The report recognizes that while each of these solutions has its own obstacles, they may still effectively address the issue. However, eCash's success in creating viable money markets depends on its ability to gain widespread acceptance and adoption. Without delving into complex details, this process would entail individuals or organizations with substantial financial resources engaging in arbitrage activities between various eCash systems, stabilizing their value relative to the underlying BTC. This positive feedback loop would boost eCash adoption, fostering more precise pricing, increased market-making, and further adoption. The cycle would repeat, driving up the use and reliance on eCash while maintaining a consistent global value.
Source: Axiom.BTC
The Potential Risks Of An eCash System
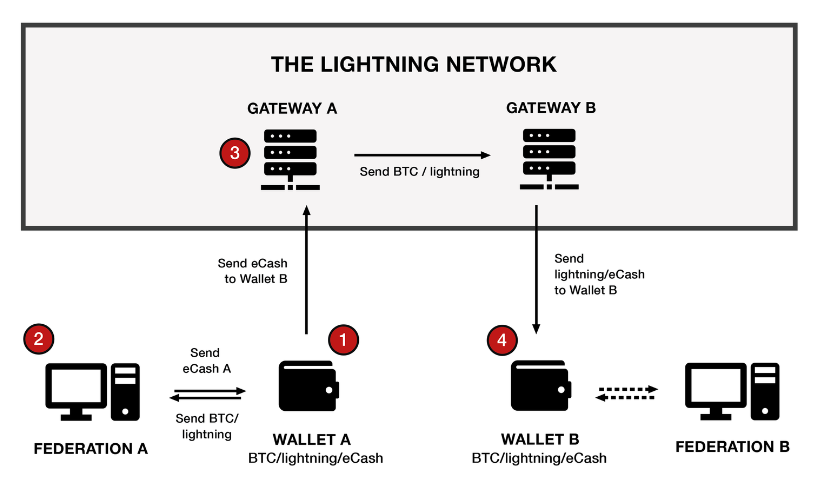
The report's third section highlights the potential risks involved with the eCash system, which is built on Bitcoin (BTC) and utilizes the Lightning Network and Fedimint technology. Eric explains that eCash is designed to be minted and redeemed for BTC on the Bitcoin blockchain or BTC on the Lightning Network using a Fedimint Network. This system should ensure that all types of eCash issued by different Fedimint networks are interchangeable and hold equal value. In other words, eCash minted for BTC using one Fedimint network's lightning Network BTC can be redeemed for Layer One BTC at another Fedimint network.
While Fedimints offers the benefit of privacy for eCash transactions, there is a potential drawback. Specifically, Fedimints can generate more eCash than the amount of BTC that backs it, which could result in an imbalance in the system. For instance, one Fedimint network might produce ten times more eCash than others, causing users to claim a disproportionate amount of BTC from other Fedimints. This issue arises because eCash is entirely private, making it difficult to keep track of the total amount in circulation. This issue is mitigated by using Cashu, which maintains a record of circulating eCash and ensures that BTC always backs it.
Now, there's already a precedent for how to solve this problem. It's called free banking, which is banking before central banks existed. In the free banking era, banks could issue currency at their own discretion. In theory, this currency was backed by gold; in practice, it wasn't always. Unfortunately, this led to a situation where customers were not always aware of the actual value of the currency they were using, as they were at the mercy of the banks' honesty. This information imbalance between banks and their customers can be compared to the privacy aspects of eCash issued by Fedimints, where the issuing authority can access more information than the users.
Source: AreaBitcoin
The caveat is that free banks did not have a widespread relationship with all individuals. Only a select few were privy to the financial workings of the free banks, and these were often the first to withdraw their funds before the system collapsed. The report highlights three such groups: competitors, brokers, and clearing houses. Eric suggests similar participants could provide comparable assurances in a decentralized eCash system. This could include entities such as Fedimints, Lightning Network gateways, eCash brokers, and even speculators who wager against unreliable Fedimints. The most crucial participant that could be introduced to an eCash system would be one capable of furnishing proof of reserves.
Those who have been involved in the crypto space since the downfall of FTX will be familiar with the emphasis placed on proof-of-reserves by exchanges aiming to enhance credibility. However, it's important to note that proof-of-reserves alone does not provide insight into a crypto exchange's obligations or debts. This means that an exchange could show evidence of holding $1 billion in BTC for its users who have deposited the same amount while simultaneously being $2 billion in debt, a detail unknown to users.
However, in an eCash system, the concept of liabilities doesn't apply in the traditional sense, as all eCash in circulation is supported by BTC held in a multi-signature wallet. The existence of this BTC collateral ensures the legitimacy of eCash minted by a Fediment, making it unnecessary to worry about liabilities.
Proof Of Liabilities
The fourth section of the report focuses on proof of liabilities. In this context, it alludes to the Cashu-created method for preserving the privacy of eCash users while monitoring the digital currency in circulation. Cashu's proof of liabilities protocol relies on three deliberate steps, which are crucial for its effectiveness.
- To publicly commit to regularly rotating its eCash private keys over a predetermined period (“epoch”). This allows all eCash in circulation to recycle from old epochs to the current epoch.
- Produce a publicly auditable list of all issued eCash tokens in the form of mint proofs.
- Produce a publicly auditable list of all redeemed eCash tokens in the form of burn proofs.
A system with these properties can ensure that Fedimint users can verify whether a mint has issued unbacked eCash during a previous epoch. This system sets an expiration date on user eCash, which prompts users to update their eCash to the latest epoch. The expiration of eCash compels users (through automated processes in their wallet software) to take actions that will lead to the mint disclosing past eCash issuance and redemptions.
The intriguing aspect is that the periodic alteration of eCash private keys is designed to mimic a bank run on the Fedimint. If the Fedimint is unable to modify the private keys used for eCash minting, it suggests that the eCash they've issued is not supported by the BTC reserves they claim.
In the fifth section of the report, Eric examines the possibility of a Bitcoin eCash system being impervious to political influence, provided that there is a sufficient number of decentralized financial networks, known as Fedimint networks. The report speculates that up to 10 million digital community banks could be in the future. Additionally, the report highlights that Fedimint networks are also resistant to politics because they are currently exempt from financial regulations but admit that this could change. If you’ve followed the crypto regulation saga, you would know that the authorities’ goal is ending all custodial crypto.
The sixth section of the report analyzes why Bitcoin and the Lightning Network are deemed inadequate. The report then shifts its focus back to comparing free banking with the eCash system in the seventh section. The risks associated with each system are highlighted in a diagram presented below.
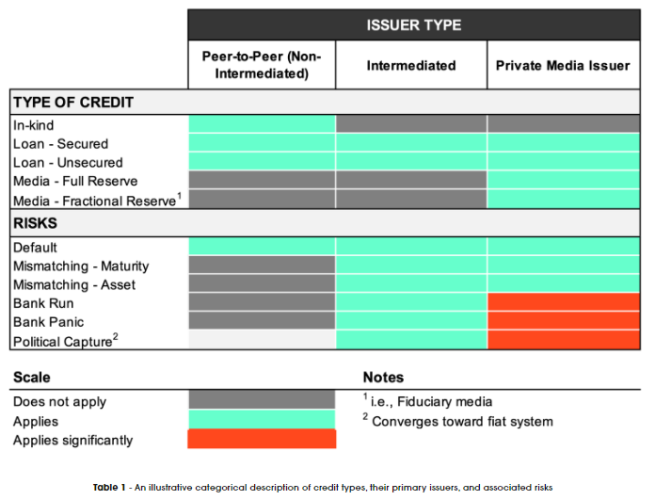
Source: Axiom.BTC
The report then discusses the potential for Fedimints to start practicing fractional reserve banking. For those unfamiliar with the concept, fractional reserve banking refers to retaining only a portion of the funds backing a currency in circulation. Most financial institutions worldwide maintain a reserve requirement of less than 30%, meaning they must hold 30 cents for every dollar they have issued.
Significantly, the Federal Reserve eliminated all reserve requirements for American banks at the onset of the pandemic and has seemingly yet to reinstate them. Eric highlights that this has raised concerns that Fedimint networks may begin operating like fractional reserve banks, meaning they would issue more eCash than BTC in reserve. However, competition among Fedimints is believed to help mitigate this risk, with those maintaining full reserves coming out on top.
Emerging Technologies
In the latter section of the report, the discussion revolves around new technologies that can bring the eCash concept to life. Eric highlights a novel protocol named Ark, currently in its conceptual phase and can be viewed as a mixing service and an onboarding mechanism that minimizes on-chain activity. Like the Lightning Network (LN) has LSPs, Ark will have Ark Service Providers (ASPs). This is a solution to the onboarding problem and a trustless custodial solution.
Interestingly, Ark's main limitation is that it can only support up to 10.5 million BTC due to technical reasons outlined in the report. Despite this, Eric believes this inherent restriction could be advantageous in the long run. The main point to remember is that Ark has the potential to overcome the technical challenges faced by the eCash system. As noted by Eric, “The Arc protocol could provide the necessary infrastructure for a trustless free banking system of service providers to emerge, removing agency from fundamental economic functions.”
Next, Eric synthesizes the information in the concluding section of the report, presenting a comprehensive overview as follows:
“Imagine a system where users dollar-cost-average into Bitcoin via Ark, use federated technology for custody, use eCash as the private cash balance for everyday transactions, and on the backend, all service providers are clearing balances between one another via the Lightning Network. Fedimints and ASPs could act as banking infrastructure, and the LN could act as the clearing houses amongst them as a hub and spoke model.”
In essence, it is a monetary framework of decentralized, community-owned, and operated digital Bitcoin banks.
What It Means For BTC
The potential impact on Bitcoin (BTC) is significant, assuming the implementation of the eCash system as described. Such a system would generate substantial demand for BTC, thereby boosting its value. In essence, the eCash aspect of this alternative financial system would serve as a powerful catalyst for BTC's growth.
The more significant concern is how this trend might impact both the financial system and your personal financial autonomy. It's important to remember that economic freedom doesn't equate to having a large sum of money. Instead, it means having the flexibility and control to make choices about your money whenever you see fit. Unfortunately, this level of autonomy is becoming increasingly scarce in traditional financial circles.
As previously stated, having a large sum of money in your bank account may hold little value if you cannot use it. When encountering someone with significant wealth, inquire about the challenges of managing such funds. The process of transferring large sums of money is complex and increasingly so. This difficulty may be attributed to the fractional reserve banking system's ongoing trend towards extreme fractionalization. Put simply, banks are putting up hurdles that make it harder to move your money around because the cash you have there doesn't even really exist.
The banking crisis from last year highlighted how convenient it is to transfer money in today's world. In the past, customers would have to physically line up at the bank to withdraw their money in the event of a problem, which is the classical definition of a bank run. Nowadays, all you need to do is click a button, which is a big problem for banks.
In any case, the growing sentiment globally is towards a financial framework that enables individuals to possess their assets and maintain their financial autonomy. The system examined in this report may or may not be the ultimate answer, but it's undoubtedly a move in the right direction toward a future where such a system will be imperative.

Image: Markethive Wallet
On The Right Side Of History
Markethive is also on the right side of history regarding financial sovereignty and keeping the entrepreneurial spirit alive. It is a domain where the individual can thrive in an expanding community of critical thinkers who uphold liberty and free expression, prioritize financial autonomy, and foster an environment where ingenuity and independence can flourish. These aspiring and seasoned entrepreneurs alike reject the constraints established financial systems impose and embrace the potential of decentralized technology.
In response to the autocracy of governments and mega-corporations on a global level, Markethive has developed its own comprehensive financial accounting hub that can be likened to a bank. This system provides users with a secure platform for financial transactions, including merchant accounts, free from the risk of account closure or seizure by authorities seeking to restrict freedom of expression for any reason.
Markethive’s evolution will include multiple sovereign servers to avoid being censured or shut down and a dynamic and innovative crypto exchange that leverages the platform's unique strengths, including innovative inbound marketing strategies, blogcasting capabilities, dynamic social engagement, and community-driven support. These endeavors are a natural progression for Markethive, allowing it to expand its reach and provide users with a seamless trading experience that integrates the platform's proven features.
With divine guidance, we will resist the oppressive totalitarian regimes that seek to subjugate humanity. Despite the power wielded by the elite, tech titans, government, and mega-corporations, a higher authority exists that eludes their control. The discerning individual cannot help but perceive the larger forces at play.
This article is provided for informational purposes only. It is not offered or intended to be used as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice.


